A common question among older adults is whether supplements for joint health are a good idea.
Maintaining joint health is crucial for ensuring mobility and a pain-free life. Healthy joints allow smooth movement, but inflammation and degeneration can lead to arthritis and osteoarthritis, which can significantly affect daily activities.
Supplements like collagen, glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids are known for their potential benefits. Though their effectiveness can vary, they may alleviate joint pain, reduce inflammation, and support cartilage health.
Drawing from my experience as a Doctor of Physical Therapy, this article covers the basics of joint health, its importance, and how supplements might help support it.
A holistic approach, including regular exercise, proper hydration, and maintaining a healthy weight, is key to optimal joint health. Let’s examine how supplements and physical therapy can work together to help you feel better.
How Do Joints Work?
Just like hinges on a door allowing a smooth and controlled motion, your joints are the connectors between your bones that allow movement. There are a few types of joints in your body, each with unique functions and ranges of motion.1
Cartilage covers the ends of your bones and protects your bones and joints. It absorbs shock, reduces friction, and supports structures in your body.
When it comes to your joints, cartilage allows your bones to move smoothly past each other. For this reason, maintaining your cartilage is vital to maintaining joint health.
Why Joint Health Matters
In my years of experience working with older adults on joint health, osteoarthritis is the number one topic of discussion.
When your joints are healthy, you can move freely and complete your daily activities without pain or restriction. But when your joint health is compromised, it can cause pain and discomfort, making it difficult to do what you want.
There’s a wide range of potential causes for joint inflammation, which leads to pain and swelling and can, depending on the cause, affect one or multiple joints.
Arthritis is an umbrella term used for conditions that cause joint inflammation. Degeneration is often due to joint wear and tear and can lead to osteoarthritis. These conditions can add serious challenges to everyday life for older adults.2
Common Supplements for Joint Health
Maintaining joint health is crucial for overall mobility and quality of life, especially for those with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Various joint supplements have gained attention for their potential to alleviate joint pain, reduce inflammation, and support cartilage health.
This section explores the benefits, effectiveness, recommended dosages, and potential contraindications of some of the most well-researched supplements for joint health, including turmeric and piperine, collagen, glucosamine and chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Turmeric & Piperine

What are Turmeric and Piperine?
Turmeric contains curcumin, a natural compound known for reducing inflammation, acting as an antioxidant, and relieving pain. Piperine (found in black pepper) helps the body absorb curcumin more effectively.
How Turmeric & Piperine Supplements Work
Curcumin helps reduce inflammation and pain, which is necessary for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Piperine enhances curcumin’s absorption, making it more effective.
Effectiveness and Research
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A study showed that curcumin with piperine significantly reduced inflammation and disease symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to a placebo.
- Muscle Recovery in Athletes: Research with elite football players found that turmeric supplements reduced muscle soreness and levels of a blood marker for inflammation (CRP) after matches.
- Osteoarthritis: Curcumin nanoparticles combined with zinc and tannic acid improved absorption and showed benefits in reducing inflammation, fighting bacteria, and protecting cartilage.
Recommended Dosage
- Dosage: 500-2,000 mg of turmeric (curcumin) daily, often taken with 5-20 mg of piperine.
- How to Take: Take turmeric and piperine supplements with meals to enhance absorption.
Contraindications
- Interactions: May interact with blood thinners, diabetes medications, and antacids.
- Allergies: People allergic to turmeric or black pepper should avoid these supplements.
Collagen

What is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein that supports parts of your body, like your skin, connective tissues, and bones. It’s the structure that holds everything together. You can find collagen naturally in foods such as chicken and bone broth.
How Collagen Supplements Work
Collagen supplements, like collagen peptides and hydrolyzed collagen, support cartilage regeneration and maintain joint health by providing the building blocks for cartilage.
Effectiveness and Research
- Joint Pain: A study published in Current Medical Research and Opinion suggests that collagen can improve joint pain in osteoarthritis patients and athletes.
- Cartilage Health: Research shows collagen supports the maintenance and regeneration of cartilage, contributing to overall joint health.
Recommended Dosage
- Dosage: 2,500-10,000 mg of collagen per day.
- How to Take: Mix collagen powder in smoothies, coffee, or water, or take in capsule form.
Contraindications
- Interactions: They are generally safe, but consult with a doctor if you are pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition.
- Allergies: People allergic to animal products should avoid collagen derived from bovine or marine sources.
Glucosamine & Chondroitin
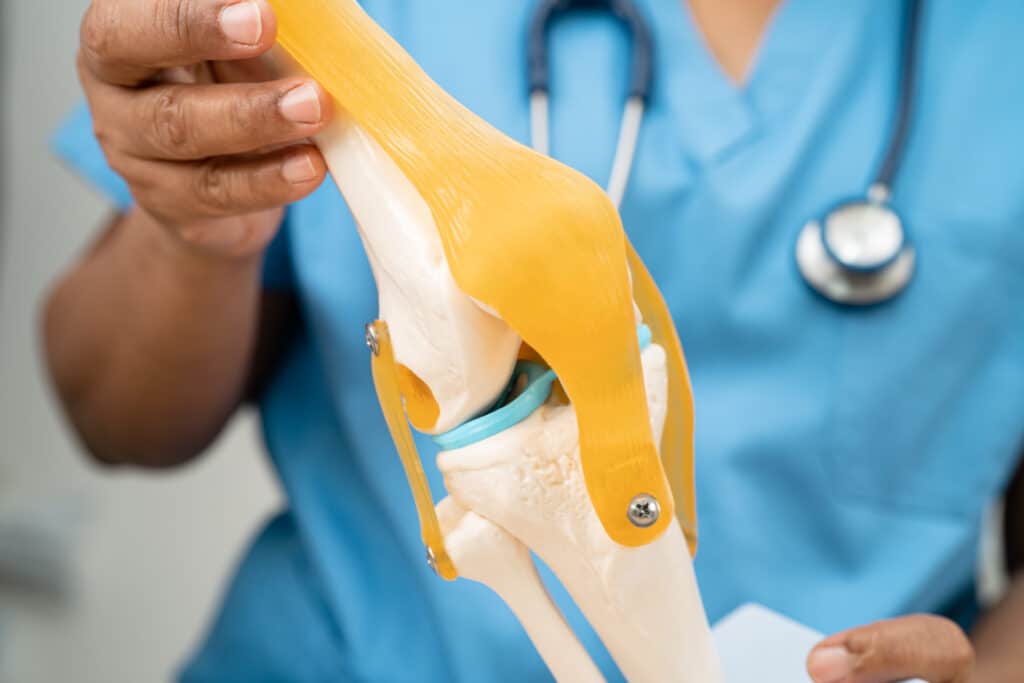
What are Glucosamine and Chondroitin?
Glucosamine and chondroitin are substances that help maintain cartilage health. They are found naturally in the body and available in supplement form.
How Glucosamine & Chondroitin Supplements Work
Glucosamine helps rebuild cartilage and maintain joint health by supporting cartilage formation and repair. Chondroitin helps keep cartilage healthy by absorbing fluid into the connective tissue and blocking enzymes that break down cartilage.
Effectiveness and Research
- Osteoarthritis: Studies suggest that glucosamine and chondroitin can help reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis, such as pain and stiffness, especially in the knee.
- Joint Health: These supplements support the structure and function of joints, promoting overall joint health and reducing the progression of joint diseases.
Recommended Dosage
- Dosage: 1,500 mg of glucosamine and 800-1,200 mg of chondroitin daily.
- How to Take: Take with meals to enhance absorption.
Contraindications
- Interactions: May interact with blood thinners, diabetes medications, and chemotherapy drugs.
- Allergies: Avoid if allergic to shellfish, as many glucosamine supplements are derived from shellfish.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
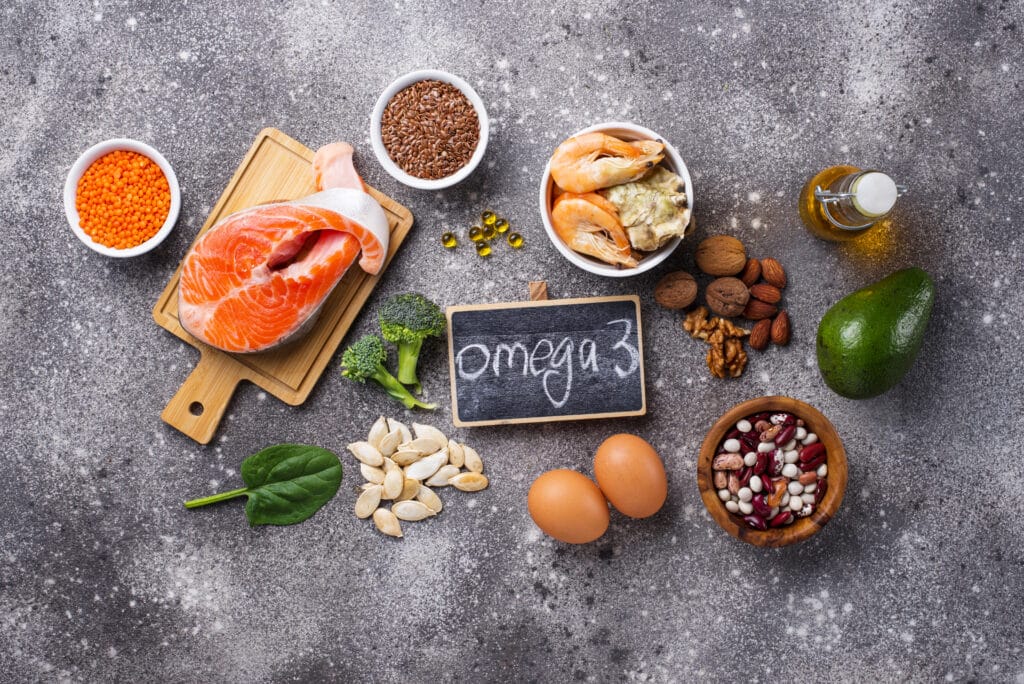

What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats in fish oil, flaxseeds, and walnuts. They help reduce inflammation, which is crucial for maintaining healthy joints.
How Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements Work
Omega-3 supplements lower joint inflammation, reducing pain and stiffness, especially in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. They also support overall joint health by decreasing the body’s inflammatory response.
Effectiveness and Research
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Studies show that omega-3 supplements can reduce joint pain and stiffness in people with rheumatoid arthritis, potentially reducing the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Osteoarthritis: Research involving 2070 patients with osteoarthritis found that omega-3 supplements significantly reduced arthritis pain and improved joint function compared to a placebo. These supplements also reduced cartilage destruction and inhibited pro-inflammatory processes, helping to slow the progression of osteoarthritis.
- General Joint Health: Omega-3s are beneficial for overall joint health. They help prevent joint problems and improve the function of cartilage and other joint tissues. They support the body’s anti-inflammatory pathways, aiding in pain relief and enhancing joint mobility.
Recommended Dosage
- Dosage: 1,000-3,000 mg of omega-3 daily, including 250-500 mg of combined EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
- How to Take: Take as an oral supplement with meals for better absorption.
Contraindications
- Interactions: May interact with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Allergies: People allergic to fish or seafood should avoid fish oil supplements and consider plant-based omega-3 sources like flaxseed oil.
While research may show promising results for these supplements in improving and maintaining joint health, it’s important to talk with your doctor before starting a new supplement regimen to determine if it’s a good fit.
If you’re anything like the patients I’ve worked with in the past, you’re probably asking, “Okay, so should I take supplements for joint health or not?”
Here’s a way to consider supplements that may help you with your long-term health and wellness goals.
Beyond Supplements: A Holistic Approach to Joint Health
Supplements like collagen, glucosamine, and hyaluronic acid may potentially benefit your joint health, but remembering that they’re just one piece of the puzzle is critical to achieving optimal health in the long run.
A holistic approach that includes regular exercise, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy weight is the foundation of joint health and contributes heavily to overall well-being.
Regular Exercise
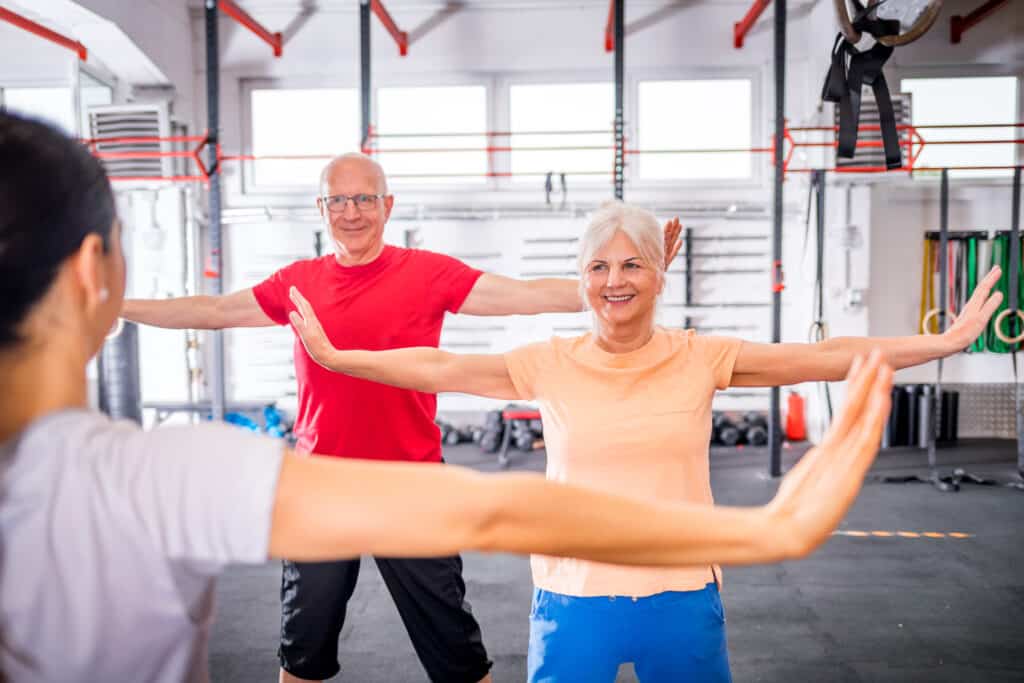

Exercise is one of the best ways to improve and maintain joint health. It helps strengthen the muscles that support joints, improves flexibility, and reduces joint stiffness.
Joint-friendly exercises that promote movement, like walking, swimming, and biking, are especially beneficial for older adults looking to improve joint health. Low-impact movements like these and strength training exercises help support joint lubrication and overall function.
Hydration
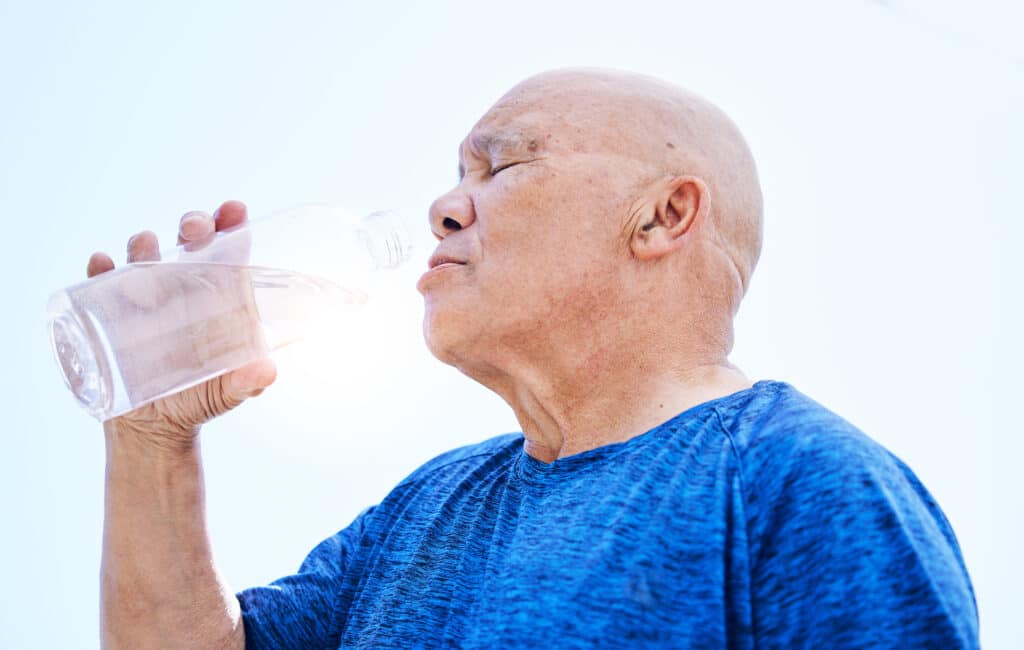

Proper hydration is an essential component of healthy joints. Your cartilage is mostly water; when dehydrated, it can become more brittle, less able to cushion your joints, and may lose its elasticity.
Water also helps lubricate joints and prevent wear and tear, which can lead to pain, inflammation, and joint stiffness. The FDA recommends about 13 cups of water daily for men and about 9 cups for women, but most of us aren’t getting nearly that much.
Weight Management
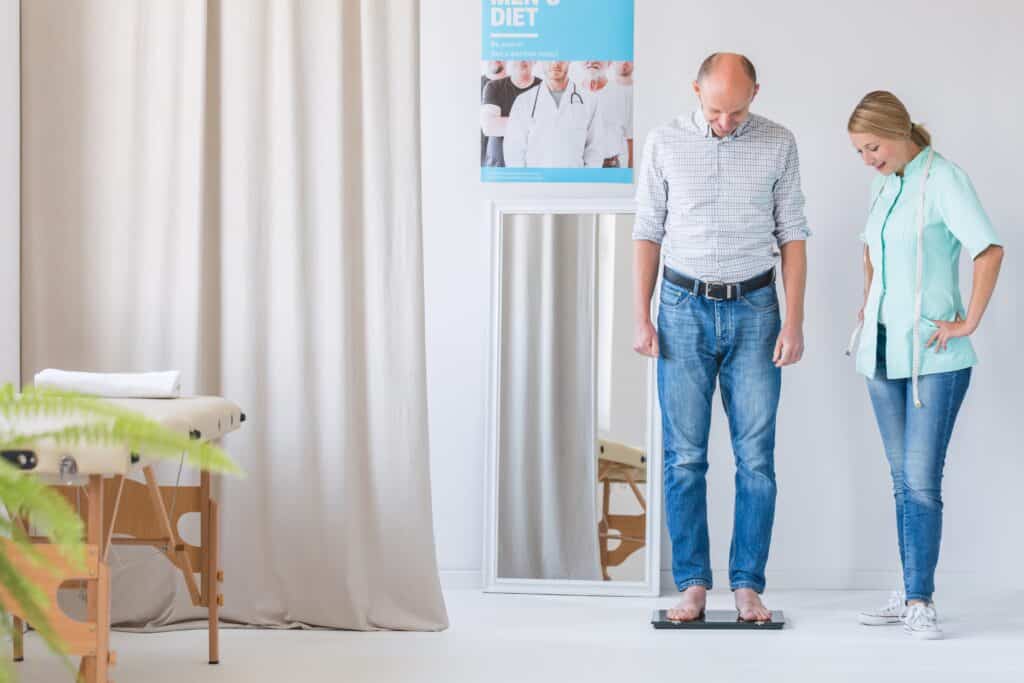

Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to keep your joints healthy. Your hips and knees are under additional stress when they support excess weight, which can increase the risk of joint degeneration.
Remember: a “healthy weight” is different for everyone, so try not to get caught up in modern beauty standards and have an honest conversation with your doctor or physical therapist about what a healthy weight means for you.
So, while supplements can offer extra support for your joints, they’re far more effective when you exercise regularly, stay hydrated, and maintain a healthy weight.
Joint Supplements and Physical Therapy
Physical therapy involves treatments and exercises designed to build strength, improve mobility, and reduce pain. It plays a major role in managing pain and maintaining joint health and can enhance the effectiveness of other joint health interventions, including dietary supplements.7
Though generally similar, physical therapists take different treatment approaches, which can include supplement recommendations.
Jimmy Lin, DPT, owner of the Forge for Athletes in Honolulu, Hawaii, recommends a high-quality turmeric supplement as an effective alternative to common over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen for those sensitive to NSAIDs.
A study published in 2023 demonstrated that older adults who used collagen supplements while participating in an exercise program saw significant improvements in joint pain and function.
These results highlight the importance of a holistic approach to joint health, incorporating supplements and healthy lifestyle choices.8
Physical therapists recommend specific exercises to train optimal movement patterns. Stretching movements can help maintain joint flexibility while strengthening exercises help keep the muscles surrounding joints strong.
However, the most important factor is learning how to move effectively using your muscles and joints. If you’re not currently working with a physical therapist to optimize the health of your joints, ask your doctor for a referral and get started as soon as possible.
Key Takeaways
- Joints allow for smooth movement, with cartilage reducing friction and absorbing shock.
- Healthy joints are key to pain-free mobility, but aging can lead to arthritis and joint degeneration.
- Supplements like collagen, glucosamine, turmeric, and omega-3s may help reduce inflammation and support cartilage health.
- Turmeric combined with piperine effectively reduces inflammation and pain, especially for arthritis.
- Collagen supports cartilage regeneration and may alleviate joint pain in older adults and athletes.
- Glucosamine and chondroitin help maintain cartilage health and reduce osteoarthritis symptoms like stiffness and pain.
- Omega-3 fatty acids reduce joint pain and stiffness while promoting overall joint health.
- Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves mobility, and complements joint supplements.
- Regular exercise, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for long-term joint health.
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements to ensure they’re right for you.
FAQs
What are the most effective supplements for joint health?
Commonly recommended supplements for joint health include glucosamine, chondroitin, collagen, turmeric (curcumin), and omega-3 fatty acids. These supplements are known for supporting cartilage, reducing inflammation, and alleviating joint pain. Glucosamine and chondroitin help maintain and repair cartilage, omega-3s reduce inflammation, and turmeric provides antioxidant benefits to combat joint issues.
Can supplements prevent or treat osteoarthritis?
While supplements may not entirely prevent osteoarthritis, research suggests they can help manage symptoms. Glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3s, in particular, have shown some potential in reducing joint pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis, particularly in the knees.
Is it safe to take multiple joint supplements at once?
Certain supplements, like glucosamine and chondroitin or omega-3s, can be safely combined with turmeric, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Some supplements may interact with medications, particularly blood thinners, or cause side effects like digestive issues. Talk to your doctor before combining ANY supplements or medications.
How long does it take for joint supplements to work?
Results from taking joint supplements can vary. Some people may see joint pain and mobility improvement within a few weeks, while others may take longer. It is often recommended to try supplements for at least 2 to 3 months before assessing their effectiveness.
Are there side effects associated with joint health supplements?
Common side effects of joint supplements can include digestive discomfort, bloating, or allergic reactions, especially in those allergic to shellfish (commonly found in glucosamine). Always consult a healthcare provider to ensure that supplements are safe based on your health condition.
Resources
- Juneja P, Munjal A, Hubbard JB. Anatomy, Joints. 2024 Apr 21. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 29939670.
- Senthelal S, Li J, Ardeshirzadeh S, et al. Arthritis. [Updated 2023 Jun 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518992/
- Martínez-Puig, Daniel, Ester Costa-Larrión, Nuria Rubio-Rodríguez, and Patricia Gálvez-Martín. 2023. “Collagen Supplementation for Joint Health: The Link between Composition and Scientific Knowledge” Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061332
- Lugo, J.P., Saiyed, Z.M. & Lane, N.E. Efficacy and tolerability of an undenatured type II collagen supplement in modulating knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr J 15, 14 (2015).
- Campos, Luana Dias, et al. “Collagen supplementation in skin and orthopedic diseases: A review of the literature.” Heliyon 9.4 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14961
- Bello, A. E., & Oesser, S. (2006). Collagen hydrolysate for the treatment of osteoarthritis and other joint disorders:a review of the literature. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 22(11), 2221–2232. https://doi.org/10.1185/030079906X148373
- Zhu X, Sang L, Wu D, Rong J, Jiang L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Jul 6;13(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0871-5. PMID: 29980200; PMCID: PMC6035477.
- Migliore A, Procopio S. Effectiveness and utility of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2015 Jan-Apr;12(1):31-3. doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2015.12.1.031. PMID: 26136793; PMCID: PMC4469223.
- Skou ST, Roos EM. Physical therapy for patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis: supervised, active treatment is current best practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019 Sep-Oct;37 Suppl 120(5):112-117. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Erratum in: Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020 Sep-Oct;38(5):1036. PMID: 31621559.
- Kviatkovsky SA, Hickner RC, Cabre HE, Small SD, Ormsbee MJ. Collagen peptides supplementation improves function, pain, and physical and mental outcomes in active adults. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2243252. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2243252. PMID: 37551682; PMCID: PMC10411303.
- Clayton, D. J., Burbeary, R., Hennis, P. J., James, R. M., Saward, C., Colledge, A., Scott, R., Gilpin, S., McMahon, R., & Varley, I. (2023). Turmeric supplementation improves markers of recovery in elite male footballers: A pilot study. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10, 1175622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2023.1175622
- Ashkan Akbari; Peyman Mottaghi; Mansour Salesi; Mehrnaz Shojaei; Gholamreza Askari; Amirhossein Sahebkar; Mohammad Bagherniya. “The Effect of Curcumin Supplementation on Clinical Factors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis”. Journal of Isfahan Medical School, 40, 700, 2023, 1052-1058. doi: 10.48305/jims.v40.i700.1052
- Deng, W., Yi, Z., Yin, E. et al. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation for patients with osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 18, 381 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-023-03855-w
- Shawl, Megan, Thangiah Geetha, Donna Burnett, and Jeganathan Ramesh Babu. 2024. “Omega-3 Supplementation and Its Effects on Osteoarthritis” Nutrients 16, no. 11: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111650




