Do you have persistent pain or discomfort in your hands and wrists?
Arthritis affects millions worldwide, causing inflammation, pain, swelling, and joint stiffness. Since we use our hands and wrist joints so often, regular wear and tear can make them especially susceptible to arthritis, which can interfere with daily tasks and activities.
In this guide, we will provide practical information on arthritis of the hand and wrist, including its definition, diagnosis, and effective treatment options.
With the knowledge and tools necessary to manage symptoms, you can improve daily function and enhance your overall quality of life so that arthritis doesn’t keep you from doing the things you enjoy.
Understanding Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
When exploring treatment or how to prevent arthritis in the hands and wrists, it’s crucial to understand the condition and its impact on joint health.
Arthritis is a common disease that leads to discomfort, inflammation, reduced mobility, and joint deformity. Various types of arthritis can affect the hand and wrist, each with distinct causes and symptoms. The most common types include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): This form of arthritis primarily affects older adults. It occurs when the cartilage covering the ends of the bones within the joints deteriorates, resulting in bone-on-bone friction and pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic joint inflammation across multiple joints. The immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the joint membrane, causing persistent discomfort.
- Psoriatic arthritis: This inflammatory arthritis occurs in some individuals with psoriasis, a skin condition marked by red, scaly patches. Psoriatic arthritis can impact the hand and wrist joints, causing pain and reduced functionality.
Symptoms of Arthritis in the Hand and Wrist
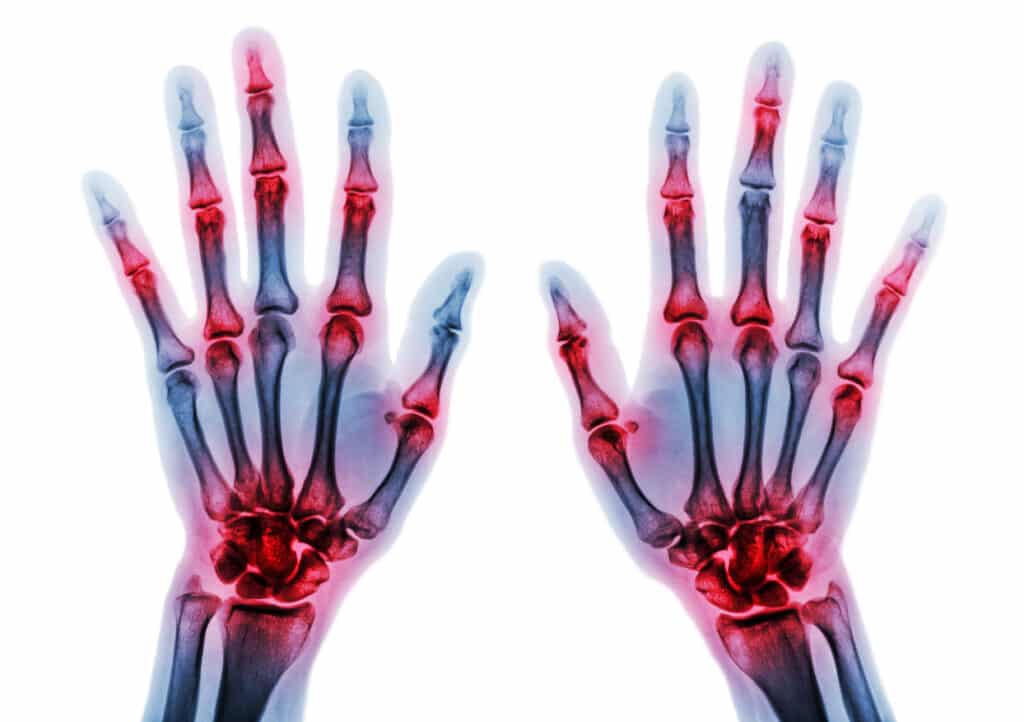
Symptoms of hand and wrist arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity. Pain is commonly one of the main symptoms and is often worsened by movement in the affected joints. Everyday activities like writing or gardening may trigger pain or discomfort, limiting your desire to do those activities.
Symptoms specific to the hands include inflammation, swelling, finger joint pain, knuckle pain, limited range of motion, erosion of bones, cartilage loss, tendon rupture, or other orthopedic issues that can visibly affect the appearance of the structures and bones of the hand and wrist.
Causes of Arthritis in the Hands
A combination of factors can contribute to the development of arthritis, including:
- Age-related changes
- Genetic predisposition
- Joint injuries
- Excessive use of specific joints
- Infections
- Abnormal immune system activity
While there is no single definitive cause of arthritis, it is considered incurable but manageable with simple lifestyle exercise and lifestyle strategies. We aim to provide accurate and reliable information to empower you to manage your arthritis self-care practice effectively.
As we delve deeper into this practical guide, we will explore effective treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate symptoms and enhance your well-being.
How is Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist Diagnosed?
If you suspect you may have arthritis in your hands and wrists, seeking a proper diagnosis is important. A doctor can confirm this condition through medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests.
Early detection and treatment of hand and wrist arthritis are crucial to prevent further joint damage, deformity, and disability. Imaging tests play a key role in diagnosing and evaluating the extent of joint damage in hand and wrist arthritis.
Standard imaging tests include X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans. These tests provide detailed images of the bones and soft tissues within the joints, helping to confirm the presence of arthritis and assess its severity.
While pain in the hands and wrists is commonly due to arthritis, it’s always best to talk to your doctor to get the best possible treatment.
Treatment Methods for Arthritis in the Hands & Wrists

Soothing Arthritis with Heat or Cold Therapy
If you’re in pain and seeking fast relief, heat and cold therapy help. These simple tools can offer soothing relief when you experience pain and stiffness in your hands and wrists.
Heat therapy relaxes muscles and improves blood flow, while cold therapy can help to reduce inflammation. You can use heating pads, ice packs, paraffin wax baths, or therapeutic gloves.
Remember to follow safety guidelines and pay attention to any precautions specific to your condition.
To apply heat or cold therapy effectively, keep the following in mind:
- Use a cloth barrier and avoid applying heat or cold directly to the skin to prevent burns or frostbite.
- Limit the treatment time to 15-20 minutes.
- Monitor your skin for signs of irritation like redness, blisters, or numbness. Stop using the therapy if you experience any of these signs.
- Individuals with poor circulation, diabetes, nerve damage, skin infections, open wounds, or heat or cold allergies should avoid thermal treatment options, as they can be harmful.
Stretches and Exercises to Keep Your Hands & Wrists Moving
Engaging in stretches and exercises can significantly improve the range of motion, muscle strength, and joint function in your hands and wrists.
Note: The following exercises are generalizations that may be helpful for some types of arthritis. Specific exercises may be recommended based on the type of arthritis you have, so consulting a physical therapist for guidance is always a good idea.
Here are a few exercises that can make a difference for your hands and wrists:
Finger flexor stretches
- Hold your hand before you, palm down, and fingers straight.
- Use your other hand to gently pull back each finger toward your wrist until you feel a mild stretch in your palm and fingers.
Spread Fingers Stretch
- Hold your hand before you, palm down, and fingers straight.
- Spread your fingers as far apart as possible, then relax
- Repeat this stretch until you feel a mild sense of fatigue in your hand.
Thumb Extension Stretch
- With your palm on a flat surface, gently grasp your thumb with your other hand.
- Pull your thumb back until you feel a stretch in your thumb and the heel of your hand.
- Be careful not to overstretch. Hold for five to ten seconds; rest and repeat as needed.
Wrist Flexion Stretch
- Hold your arm straight before you with your palm facing down.
- With your opposite hand, press the back of your hand toward the floor until your fingertips are pointing toward the floor.
- Hold the stretch for ten to twenty seconds, then release. Repeat as needed.
Grip strengthening
- Hold a foam ball or towel and squeeze it as hard as possible without causing pain.
- Try multiple variations (as seen in the video) with palms facing up or down. Using a slight rotation motion also helps to strengthen the wrists.
- This simple exercise can be done frequently throughout your day.
Low-impact aerobic activities
Engage in activities like walking, swimming, or cycling to increase your heart rate and blood circulation without exerting excessive stress on your joints. These activities can reduce inflammation, improve oxygen delivery, enhance mood, and promote weight loss.
Kinesiotaping for Relief
Research has shown that combining exercise with Kinesio taping techniques can enhance their effectiveness. Your physical therapist can assist with the proper placement and tension of the tape, leading to improved outcomes and reduced pain. [5]
(If you need to become more familiar with kinesiotape, look at this article to learn more about this method and how it might be helpful for you.)
Splints and Braces: Giving Your Joints the Support They Need
Splints and braces can be very helpful when your joints require extra support. These devices restrict excessive movement, alleviate pain and inflammation, and stabilize your wrist and finger joints.
Everybody is different, so it’s important to select the correct size device, wear them correctly, and use them only as necessary. Talk to your physical therapist to get correctly fitted for a brace.
Several types of splints and braces are available, including:
- Thumb spica splints cover the thumb and part of the wrist, specifically targeting arthritis at the base of the thumb. They enhance grip strength, dexterity, and overall comfort.
- Finger splints cover one or more fingers, treating arthritis in the middle or end joints and preventing deformity. They limit joint movement and reduce pressure, helping to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Wrist splints cover the wrist and part of the hand, addressing arthritis in the wrist. They improve functionality and stability by maintaining a neutral and optimal position for the wrist.
- Compression gloves provide gentle graded pressure and effectively manage arthritis in the hand and wrist. They reduce swelling, improve blood circulation, and enhance comfort.
Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider for the proper use of a splint or brace, and regularly examine it for wear and tear. Remove the splint or brace periodically to allow your skin to breathe and prevent moisture buildup.
Alternative Therapies: Thinking Outside the Box

If you’re open to trying alternative therapies, some options may relieve hand and wrist arthritis. Before attempting these therapies, it’s essential to understand the evidence and potential risks associated with them.
Alternative therapies stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms, enhance the mind-body connection, or promote relaxation and comfort.
Acupuncture
This practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture can help relieve pain by stimulating nerves, muscles, and connective tissues, as well as promoting the release of endorphins.
Massage therapy
By applying pressure or vibration to soft tissues in the body, massage therapy can help reduce aches and pains. It improves blood circulation, reduces muscle tension, and can help to mediate pain for arthritic joints.
Injections: Targeting the Pain
When conservative measures are not working, injections can deliver medication directly into the hand or wrist joints, targeting pain and inflammation caused by arthritis.
The two most common injections for hand and wrist arthritis are corticosteroid and hyaluronic acid injections.
Corticosteroid injections
These contain potent anti-inflammatory medication. When injected directly into the affected joint, injections relieve pain and decrease swelling. However, their effects are temporary, typically lasting a few months, and repeated injections may be necessary.
Hyaluronic acid injections
Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of joint fluid that acts as a lubricant and shock absorber. These injections aim to replenish diminished hyaluronic acid in the joint, reducing pain, improving joint movement, and relieving arthritis symptoms.
Multiple injections over several weeks may be required, and results can vary.
Medications: A Helping Hand
Medications are often crucial in managing pain associated with hand and wrist arthritis.
From over-the-counter pain relievers to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for rheumatoid arthritis, a range of options is available. It is essential to work closely with your doctor to find the proper medication and dosage that suit your needs.
Different types of medications used for arthritis pain in the hands and wrists include:
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Advil or Aleve, reduce pain and inflammation. While they offer fast and effective relief, prolonged use may lead to side effects such as stomach ulcers, bleeding, or kidney damage.
- Acetaminophen: Commonly known as Tylenol, acetaminophen provides mild to moderate relief but can cause liver damage with continued use.
- Opioids: These medications offer strong and long-lasting pain relief but have side effects such as constipation, nausea, drowsiness, or addiction.
- Topical analgesics: Available as creams, gels, sprays, or patches, these products provide local and temporary pain relief. Proper application is essential to avoid skin irritation or burning.
Before using any medication, it is vital to consult your doctor and follow their instructions on proper and safe usage.
Surgery: The Last Resort

In severe cases of arthritis where other treatments have not been helpful, surgery may be considered a last resort. Surgical procedures can help restore function and reduce pain when conservative measures have been exhausted.
Before deciding on surgery, it is important to thoroughly discuss the benefits, risks, and potential complications of surgery with your healthcare provider.
Surgical options for arthritis include:
Arthroscopy
This minimally invasive surgery involves inserting a thin tube with a camera and instruments into the joint through small incisions. It can be used for diagnostic purposes and to treat joint problems such as inflammation, infection, loose bodies, or cartilage damage.
Joint fusion
This procedure involves joining two bones within the joint using screws, plates, or wires. Joint fusion improves stability by eliminating excessive movement and friction in the joint. It can also help correct deformities or contractures by aligning the bones properly.
Joint replacement
This surgery entails removing the damaged or diseased parts of the joint and replacing them with artificial components. Joint replacement can reduce pain and improve joint function by restoring smoothness and mobility.
How to Prevent or Delay Arthritis of the Hand & Wrist
Prevention is always preferable to treatment. Regarding hand and wrist arthritis, specific lifestyle changes can help prevent or delay its onset or progression.
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in joint-friendly exercises, protecting your hands from injuries, and managing stress are all ways to care for your joints. It is always possible to incorporate these changes into your daily life and prioritize the well-being of your hands and wrists.
The Role of Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking reduces blood flow to the joints, while alcohol hampers calcium and vitamin D absorption, both crucial for bone and cartilage health.
Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can improve blood circulation and enhance bone density, delaying the onset of arthritis. These behaviors have been proven to cause a number of health problems, so moderation is beneficial regardless of your health status.
Key Takeaways
- Arthritis is a common disease affecting the hand and wrist, leading to discomfort, inflammation, reduced mobility, and joint deformity. The types include Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Psoriatic arthritis.
- Symptoms of hand and wrist arthritis include pain, inflammation, swelling, and limited range of motion. It can impact everyday activities like writing or gardening.
- Arthritis can be caused by various factors such as age-related changes, genetic predisposition, joint injuries, infections, and abnormal immune system activity.
- Hand and wrist arthritis is diagnosed through medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans.
- Various treatment strategies can be used to manage arthritis symptoms, including heat and cold therapy, exercises and stretches, kinesiotaping, splints and braces, and alternative therapies like acupuncture and massage therapy.
- In more severe cases, injections, medications, and even surgery (arthroscopy, joint fusion, joint replacement) can manage the pain and restore function.
- Regardless of the treatment option, working closely with your healthcare provider for the best results is essential.
FAQs
What other conditions can cause symptoms similar to arthritis of the hand and wrist?
Several conditions can mimic the symptoms of arthritis in the hands and wrists. These include carpal tunnel syndrome, ganglion cysts, tendonitis, and other repetitive stress injuries. Other systemic diseases, such as lupus or gout, can cause similar symptoms. Getting a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is essential to ensure the right treatment approach.
How does arthritis in the hands and wrists affect one’s ability to engage in hobbies or sports?
Arthritis in the hands and wrists can affect grip strength, fine motor skills, and overall joint mobility, limiting participation in hobbies and sports. Activities requiring precise hand movements, such as playing a musical instrument, knitting, or golfing, may become more challenging. However, with proper management strategies such as using assistive devices, modifying activities, and engaging in appropriate exercises, many people with arthritis can continue to enjoy their hobbies and sports.
What are the risks or potential complications associated with the long-term use of braces or splints?
Long-term use of braces or splints can sometimes lead to issues such as skin irritation, muscle atrophy due to lack of use, or joint stiffness from reduced mobility. Some people may also develop a dependency on these devices. It’s important to use these devices as advised by a healthcare professional and continue strengthening and mobility exercises as part of a balanced treatment plan.
How does weather or climate impact symptoms of arthritis in the hands and wrists?
Some people with arthritis report that their symptoms worsen in cold, damp weather or when atmospheric pressure changes, such as before a storm. The exact reason for this isn’t clear, but it might be due to changes in barometric pressure affecting the pressure inside the joints. However, this varies significantly from person to person, and not everyone with arthritis is affected by weather or climate changes.
What factors should I consider when choosing between alternative therapies and more conventional treatments for arthritis in the hands and wrists?
When choosing between alternative therapies and conventional treatments, consider factors such as the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, the potential side effects or risks of the treatments, and your preferences. Discussing these options with your healthcare provider is essential, as some alternative therapies can interact with conventional medications or may not be suitable in some cases.
Are there support groups or resources available for individuals struggling with arthritis in the hands and wrists?
Yes, many support groups and resources are available for people with arthritis. Organizations like the Arthritis Foundation offer resources, educational materials, and connections to local support groups. Online communities and forums can also support and advise people experiencing similar challenges. Physical therapists, occupational therapists, and social workers can also provide valuable resources and strategies for managing life with arthritis.
References:
- Grunz JP, Gietzen CH, Christopoulos G, van Schoonhoven J, Goehtz F, Schmitt R, Hesse N. Osteoarthritis of the Wrist: Pathology, Radiology, and Treatment. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2021 Apr;25(2):294-303. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1730948. Epub 2021 Aug 9. PMID: 34374064.
- Akhondi, H., & Panginikkod, S. (2022). Wrist arthritis. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531497/




